
A chiller is a type of air conditioning or refrigeration system that is used to cool air or liquids. It is commonly used in various industries, including commercial buildings, data centers, and laboratories, as well as in residential settings. In this article, we will discuss how a chiller works, its components, and its advantages.
Chiller Components
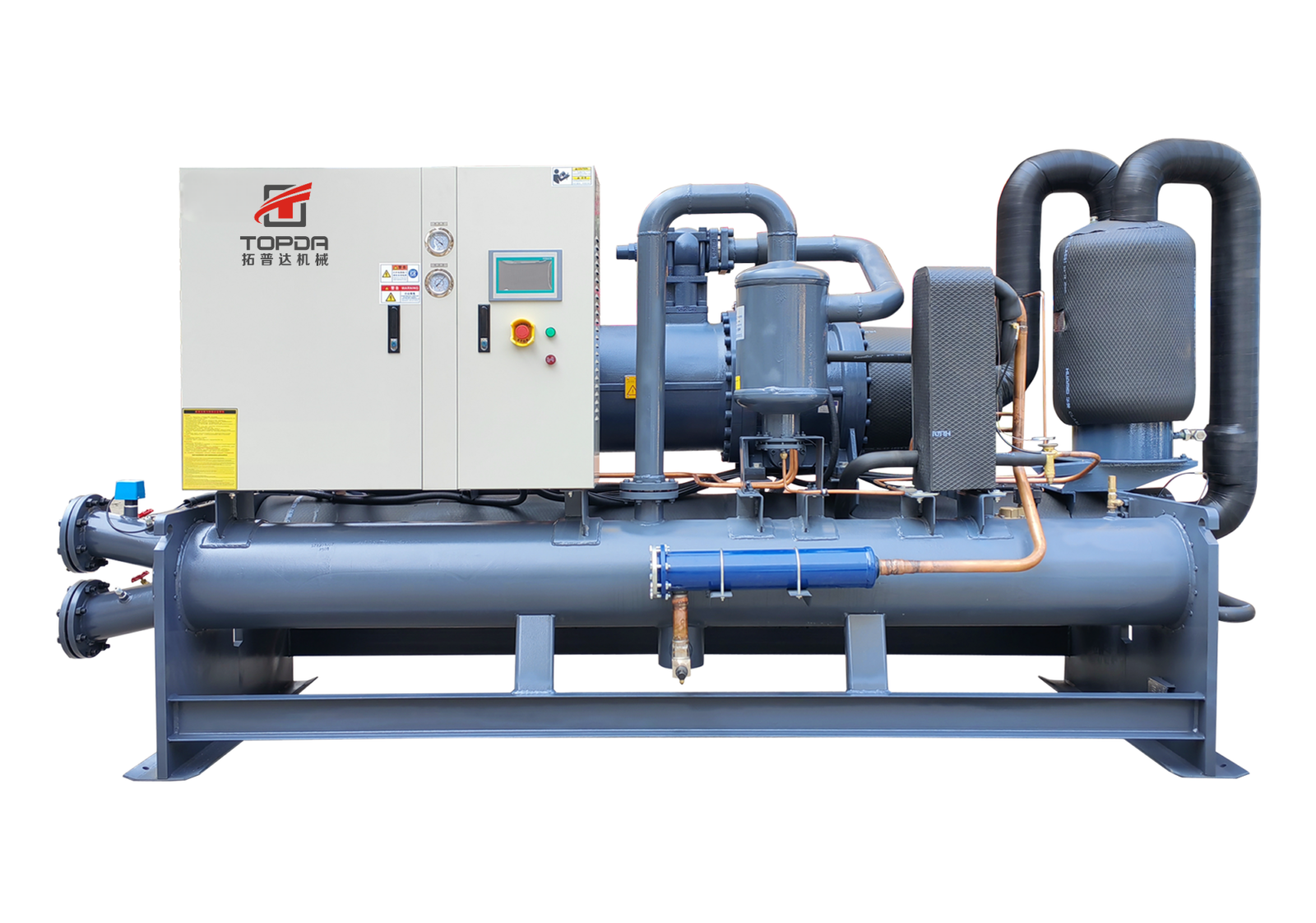
A typical chiller consists of the following components:
- Compressor: This is the heart of the chiller, responsible for compressing the refrigerant. It is typically located in the outdoor unit and is responsible for the cooling process.
- Pump: The pump is used to circulate the refrigerant through the system. It is typically located in the indoor unit and is responsible for circulating the refrigerant throughout the system.
- Cooling Coil: This is where the heat is transferred from the air or liquid being cooled to the refrigerant. It is typically located in the indoor unit and is responsible for the cooling process.
- Refrigerant: This is the substance that is used to transfer heat from the air or liquid being cooled to the outside air or a cooling source. Common refrigerants include Freon, R-410A, and CO2.
How a Chiller Works
The cooling process in a chiller works as follows:
- The compressor compresses the refrigerant, causing it to become hot and high-pressure.
- The hot, high-pressure refrigerant is then directed to the condenser coil, where it releases its heat to the outside air and condenses back into a liquid.
- The cooled refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and allows it to expand.
- The cold, low-pressure refrigerant then enters the evaporator coil, where it absorbs heat from the air or liquid being cooled and evaporates into a gas.
- The now-hot, high-pressure refrigerant is then directed back to the compressor to start the cycle again.
Advantages of Chillers
Chillers have several advantages, including:
- High cooling capacity: Chillers are capable of cooling large volumes of air or liquid quickly and efficiently.
- Flexibility: Chillers can be used in a variety of applications, including air conditioning, data centers, laboratories, and industrial processes.
- Reliability: Chillers are designed to be highly reliable and require minimal maintenance.
- Energy efficiency: Chillers are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing the need for additional cooling sources.
結論
In conclusion, chillers are complex systems that use refrigeration to cool air or liquids. They consist of several components, including compressors, pumps, cooling coils, and refrigerants. The cooling process works by compressing and expanding the refrigerant, which allows for the transfer of heat from the substance being cooled to the outside air or a cooling source. Chillers have several advantages, including high cooling capacity, flexibility, reliability, and energy efficiency. By understanding how a chiller works and its advantages, you can better determine whether it is the right choice for your cooling needs.
よくある質問
Q: What is the difference between a chiller and an air conditioner?
A: A chiller is a more complex system that cools large volumes of air or liquid, while an air conditioner is designed to cool a smaller space, typically a single room or office.
Q: Can a chiller be used for both air and liquid cooling?
A: Yes, a chiller can be used for both air and liquid cooling, depending on the design and configuration of the system.
Q: How do I choose the right chiller for my needs?
A: To choose the right chiller for your needs, consider factors such as the size of the area or volume to be cooled, the temperature range required, and the level of cooling required. It is also important to consult with a professional to ensure the chiller is properly sized and designed for your specific needs.
Q: How do I maintain my chiller?
A: Regular maintenance is important to ensure the chiller operates efficiently and effectively. This includes regular cleaning of the condenser coils, checking refrigerant levels, and performing routine maintenance on the compressor and pump.











返信を残す