
How Do Air-Cooled Water Chillers Work?
Air-cooled water chillers are widely used in various industries, including IT, healthcare, data centers, and more, to cool electronic equipment and keep it running at optimal temperatures. In this article, we’ll delve into the inner workings of air-cooled water chillers and explore how they maintain a stable and consistent temperature for your valuable equipment.
The Basics of Air-Cooled Water Chillers
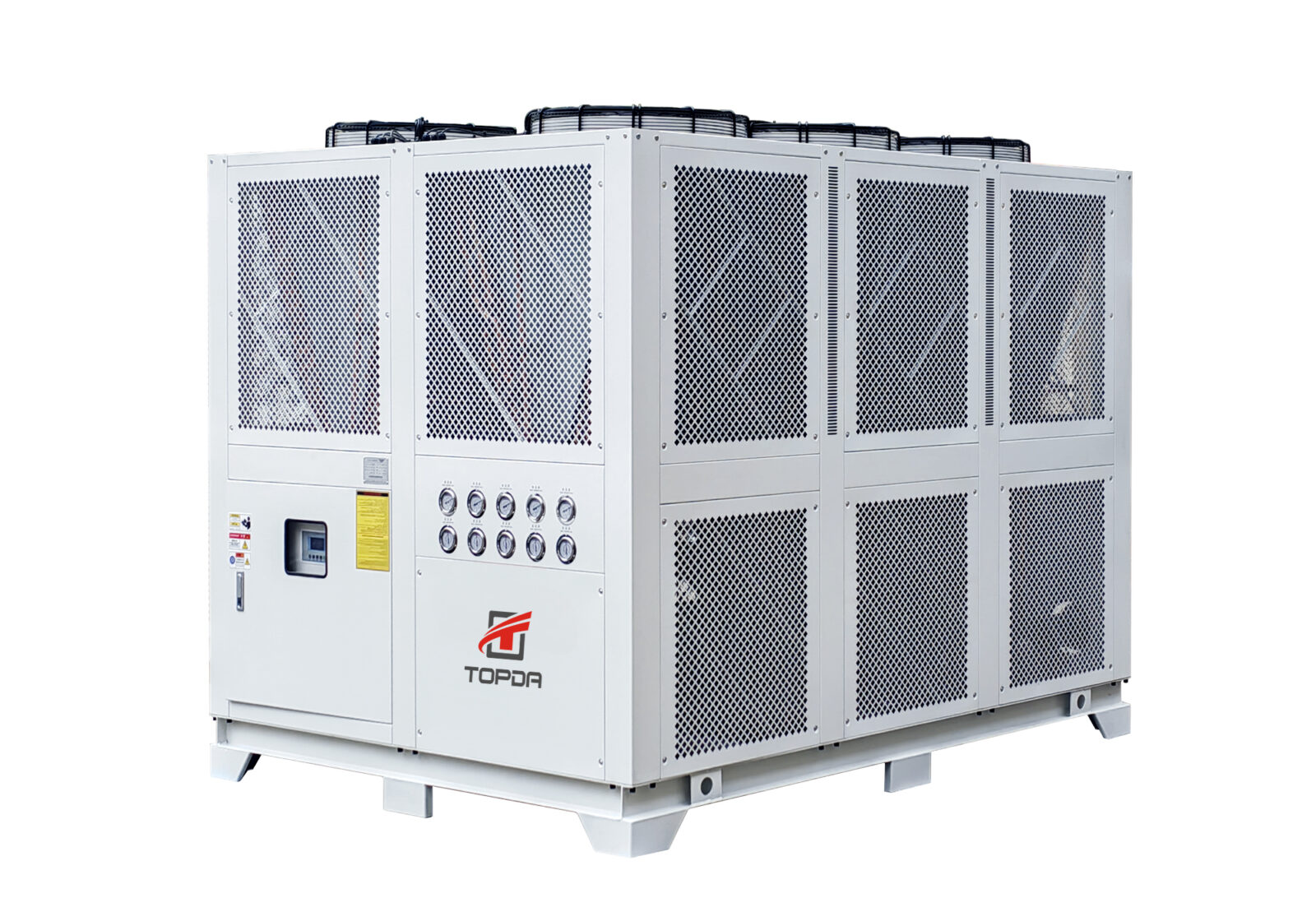
Air-cooled water chillers are designed to cool water, which is then used to cool electronic equipment, such as servers, servers, and other IT equipment. They work on the principle of heat transfer, where a liquid coolant (usually water or a water-based solution) absorbs heat from the equipment and transfers it to the surrounding air, which is then dissipated outside the building or facility.
There are two primary components of an air-cooled water chiller:
-
Condenser Coil:
This coil is responsible for rejecting the heat from the coolant to the surrounding air. It’s typically located outside, where there’s ample airflow and a small temperature difference between the coil and the surrounding air. -
Evaporator Coil:
This coil is responsible for absorbing heat from the coolant and transferring it to the chiller’s refrigerant. It’s usually located inside the chiller, where it’s close to the equipment being cooled.
The Cooling Process
The cooling process in an air-cooled water chiller works as follows:
-
Step 1: Heat Absorption:
The coolant absorbs heat from the equipment being cooled and transfers it to the evaporator coil. -
Step 2: Heat Transfer:
The heat is then transferred from the evaporator coil to the refrigerant, which is typically a mixture of air and a refrigerant, such as Freon or ammonia. -
Step 3: Heat Rejection:
The refrigerant-transferred heat is then rejected by the condenser coil, which is located outside the chiller and exposed to the surrounding air. -
Step 4: Cooling Repeat:
The cooling process is repeated continuously, with the refrigerant returning to the evaporator coil, absorbing more heat, and restarting the cycle.
How Air-Cooled Water Chillers Maintain a Stable Temperature
Air-cooled water chillers maintain a stable temperature by closely monitoring and controlling the refrigerant’s temperature and pressure. This is achieved through:
-
Thermostats and Temperature Sensors:
These devices monitor the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant and coolant to ensure optimal operation. -
Pumps and Valves:
These components control the flow of refrigerant and coolant to maintain a consistent temperature and pressure.
Conclusión
In conclusion, air-cooled water chillers play a crucial role in maintaining a stable and consistent temperature for various industries and applications. By understanding the basic principles of how they work, including the components, cooling process, and temperature control mechanisms, you can make informed decisions when selecting an air-cooled water chiller for your specific needs.
Preguntas frecuentes
FAQ 1: What is the primary advantage of air-cooled water chillers?
The primary advantage of air-cooled water chillers is that they can be used in a variety of environments, including data centers, laboratories, and industrial settings, without requiring the need for a separate cooling tower or other external cooling system.
FAQ 2: What is the characteristic of air-cooled water chillers that sets them apart from other types of chillers?
The characteristic that sets air-cooled water chillers apart is the way they dissipate heat, which is done directly to the surrounding air, rather than to a secondary fluid or gas, as is the case with other types of chillers.
FAQ 3: What are some common applications for air-cooled water chillers?
Some common applications for air-cooled water chillers include data centers, laboratories, hospitals, and industrial settings, where precise temperature control is required to ensure the optimal performance of equipment and maintain a stable environment.
FAQ 4: What are the potential benefits of using an air-cooled water chiller?
Some potential benefits of using an air-cooled water chiller include:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Increased reliability and uptime
- Space and cost savings
FAQ 5: What are the potential drawbacks of using an air-cooled water chiller?
Some potential drawbacks include:
- Higher maintenance costs
- Noise and vibration from the cooling fan
- Potential for air leaks or corrosion











Dejar una respuesta